
Background Image inspection of truck tyres Help and Advice
Inspection des pneus sur un camion
The right tire pressure for trucks and buses
Selecting the correct tire pressure is essential to maintaining tire performance
Tires are the only point of contact between your vehicle and the road.
It is vital to the safety of a driver, as well as the goods they transport. And depending on the temperature, work and load conditions, there is only one. It's tire pressure.
So, it’s important to find the right tire pressure. Air pressure is an essential element for properly functioning tires, enabling passengers and/or the load to be carried in a way that is:
- safe
- reliable
- economical
- comfortable
However, from various tests and inspections facilitated by MICHELIN, tire pressure often appears to be one of the least monitored maintenance issues.

Michelin Picto tire inflation 1 Tire
TIRE INFLATION BASICS. PROPER INFLATION: THE MOST IMPORTANT STEP OF TIRE MAINTENANCE.
Many of today's tire problems are caused by insufficient or careless attention to tire pressures. No tire or tube is completely impervious to loss of air pressure. To determine the proper inflation pressure, all trucks should be weighed.
HOW TO WEIGH YOUR TRUCK
Be sure to weigh your vehicles, fully loaded, on a scale. Each axle, front and rear, and trailer must be weighed separately. Actual gross axle weights should be compared with the manufacturer's tire data book to determine the inflation pressure required.
The load carried by each individual front axle tire should be noted. If the maximum load-carrying capacity of the tire is below the actual scale weight, greater carrying capacity tires must be used, either a higher load index (load range or ply rating) or a larger tire size.
Pressure and Safety
Improper tire pressure can negatively impact fundamental safety features, such as:
- The strength of the carcass
- Vehicle stability and handling
- Vehicle grip
- Resistance “curb bumps”
Change in Tire Pressure
During operation, tires can lose pressure for various reasons:
- Rim sealing (e.g. cracks or welds)
- Cuts or perforations
- Natural permeation through tire parts
In addition to in-vehicle control systems, visual inspection and periodic pressure checks with a pressure gauge is the most common way of detecting possible air loss problems.
Check Your Tire Pressure
Inspection must include all tires on the vehicle (including the spare tire)
- Insufficient tire pressure leads to an abnormal rise in the operating temperature and may cause deterioration of internal parts. This deterioration is irreversible and may cause the tire failure with rapid air loss. Consequences of driving with insufficient tire pressure may not be immediately visible and may become apparent even after an issue has been corrected.
- Insufficient tire pressure also increases the risk of hydroplaning or possible accident.
- Over inflation can cause rapid and uneven wear and an increased probability of road hazard damage (tread damage, carcass breakage).
- Using Nitrogen does not reduce the need to check tire pressure frequently (at least once a month).
In all cases, the air pressure recommended by the vehicle or tire manufacturer must be followed. Tire pressure should always be adjusted to load and specific tire use.
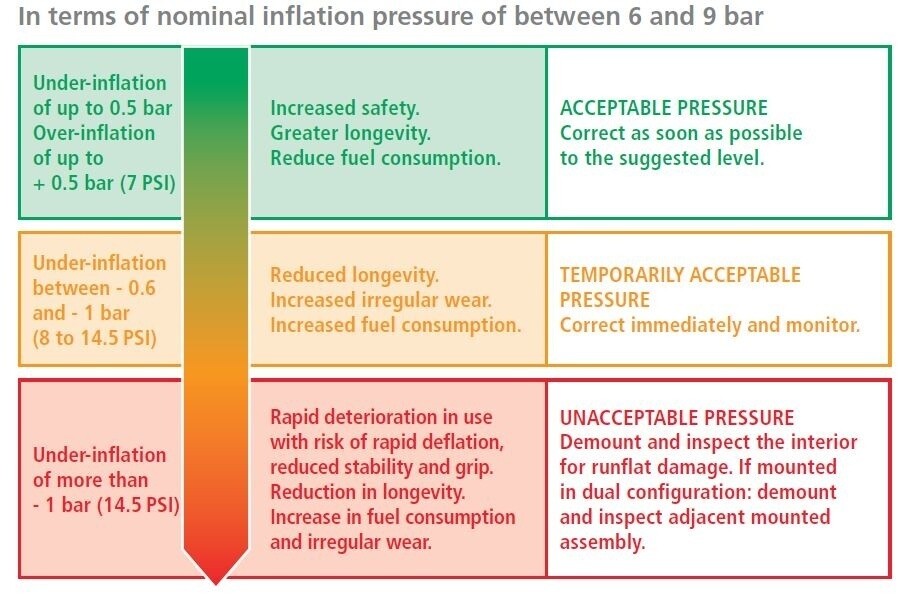
Picto la juste pression page 72 Help and Advice
pressure table
Important Precautions
- Check air pressure when tires are cold.
- Tire pressure increases while driving; never deflate the pressure of a hot tire.
- Never reflate a tire that has been under-inflated without a thorough internal/external inspection of the tire.
- Cold tire pressure higher than 145 psi is not recommended.
- If cold tire pressure is over 8 psi the recommended pressure, tire pressure should be corrected immediately.
- In all cases, comply with local regulations and laws.
- Use an accurate, calibrated pressure gauge and handle with care.
- If a tire checked in warm conditions has a lower pressure than recommended, the tire must be disassembled and checked in accordance of safety instructions.
- If one tire appears significantly hotter than the others, it must be dismantled and checked following the same safety instructions.
- Tire air pressure on the same axle should normally be of the same pressure (depending on tire size).
- Tire pressure must be checked 24 hours after installation and must not be more than 5 % lower than the original pressure.
- Follow tire pressure recommended by the vehicle manufacturer or manufacturer of your tires.
Picto inflation Help and advice
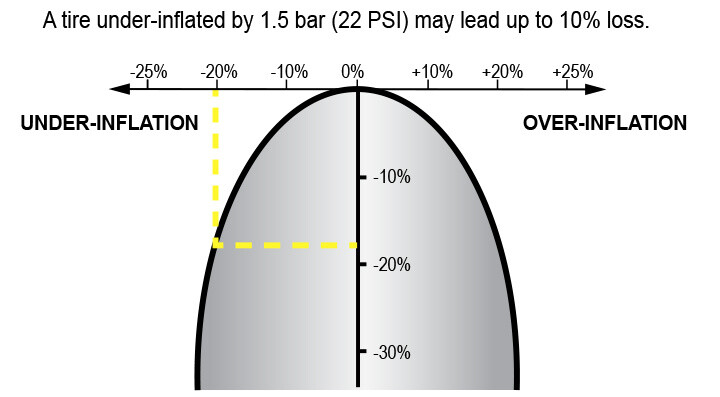
Impact of Tire Pressure on Mileage
Under-inflation of 22 psi = 10% yield loss
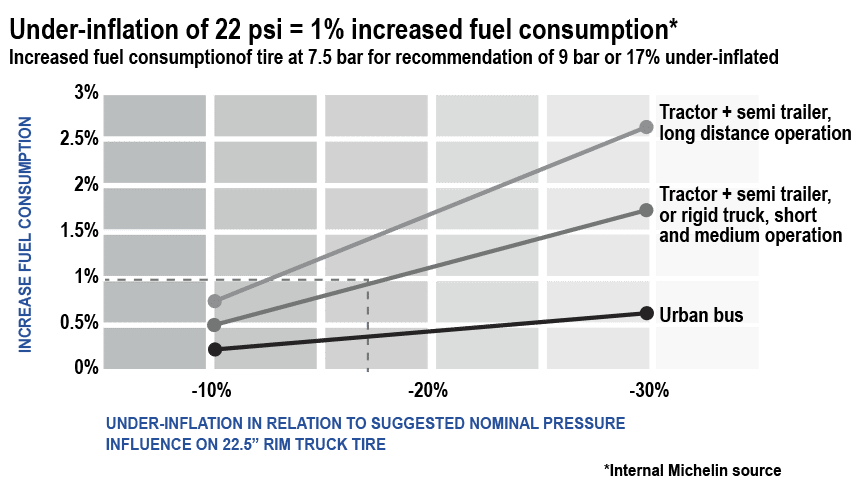
Impact of Tire Pressure on Fuel Consumption
Tire pressure has a proven impact on fuel consumption. Incorrect tire pressure increases tire rolling resistance impacting the vehicle's fuel consumption.
Under-inflation of 22 psi = 1 % increased consumption
For example, tire pressure at 109 psi for a tire that should be at 131 psi (17% under inflated) can impact fuel consumption up to 1%.
Picto bar inflation Help and Advice
These tips and suggestions may also be of interest:
• Tire Basics and Markings
• Tire Structure and Functions
• Application Tips




